Your BMI guide starts here. BMI (Body Mass Index) is a weight-to-height ratio. Healthcare providers use it for initial health screening. The CDC states it’s a reliable indicator of body fatness for 90% of people.
What is BMI?
BMI (body mass index) is a measure used to estimate whether a person’s weight is healthy for their height. Understanding your BMI can help assess your health risks and guide weight management. This beginner’s guide will cover the key things you need to know.
BMI stands for body mass index. It is a calculation using your weight and height to estimate your total body fat.
BMI is used as a screening tool to indicate if a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. It can assess your risk for developing certain diseases that are linked to higher body fat.
Here is the formula to calculate your BMI:
⚡ Key Takeaways
- Understand that BMI is a screening tool that estimates if your weight is healthy for your height by calculating body fat percentage.
- Calculate your BMI using weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared, or use online calculators and charts for convenience.
- Aim for the healthy range (18.5-24.9) which is linked to the lowest risk for chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
- Monitor your BMI regularly to assess health risks, guide weight management goals, and track progress over time.
- Recognize the limitations – BMI is a screening tool that should be used alongside other health assessments for a complete picture.
- Use BMI as motivation to make informed decisions about nutrition and exercise to achieve or maintain a healthy weight range.
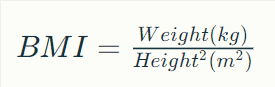
For a person weighing 68 kg with a height of 1.75 meters, the BMI calculation is:
Why is BMI a Critical Health Metric in 2026?
Tracking your Body Mass Index provides a foundational health snapshot, helping to:
- Assess your risk for developing obesity-related diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers
- Guide you on if you need to gain or lose weight to reach a healthier range
- Track your progress with a tool like MyFitnessPal or Apple Health if you are actively managing your weight.
- AI-powered online calculators from sources like the CDC or WHO.
- Integrated health apps on your Garmin or Fitbit device that sync BMI with your activity data.
However, the standard BMI formula has well-documented limitations, which we will detail in a later section. For a complete health picture in 2026, it should be used alongside other metrics like body fat percentage and waist-to-height ratio.
How to Calculate Your BMI in 2026
You can calculate your BMI instantly using one of these modern methods:
However, BMI has some limitations which are discussed later. It should be used along with other health assessments.
How to Calculate Your BMI
You can easily calculate your BMI using:
- Online BMI calculators
- BMI charts that compare weight ranges to height
- Use the mathematical formula if you have your precise weight and height measurements.
- Weight must be measured in kilograms (kg).
- Height must be measured in meters (m).
To correctly apply the BMI formula, you need accurate inputs:
For a quick calculation, you can use a dedicated BMI tool.
Your resulting score places you in a weight status category, which correlates with specific health profiles and potential risks for 2026.
To determine the numbers to plug into the BMI formula:
- Weight should be measured in kilograms (kg)
- Height should be measured in meters (m)
Here is a BMI calculator widget you can use to calculate your score:
Once you calculate your BMI, you can categorize your weight status and understand potential health risks.
| BMI Range | Weight Status | Health Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight | Nutritional deficiency, osteoporosis, decreased immunity |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Healthy Weight | Least risk for developing obesity-related diseases |
| 25.0 – 29.9 | Overweight | Increased risk for heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes |
| 30.0 and above | Obese | High risk for developing serious medical conditions like heart disease, diabetes, cancer |
As the data indicates, maintaining a BMI within the healthy range of 18.5–24.9 is strongly correlated with the lowest long-term risk for chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Achieving this should be a primary health objective, supported by consistent, sustainable lifestyle habits.
Limitations of BMI
While BMI remains a widely used screening tool, its key limitations for 2026 include:
- It does not differentiate between fat, muscle, and bone mass
- BMI may overestimate body fat in athletes/muscular builds
- BMI may underestimate body fat in older adults who lose muscle
- It fails to account for critical fat distribution patterns, such as visceral versus subcutaneous fat.
- Commit to consistent, varied movement – The 2026 WHO guidelines recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly, such as brisk walking or cycling. This regimen is proven to optimize caloric expenditure and build metabolically active lean muscle mass.
- Prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods – Base your diet on fruits, vegetables from the Brassica family, and ancient whole grains like quinoa and farro. These foods deliver essential vitamins, minerals, and high-volume fiber to promote satiety and reduce overall caloric intake.
As of 2026, BMI remains a population-level screening metric, not a diagnostic tool. Relying on it in isolation misses over 25% of cardiometabolic risk cases. For a complete health picture, clinicians now combine it with waist circumference and DEXA-scanned body fat percentage. A landmark 2025 meta-analysis in Obesity confirmed the waist-to-height ratio predicts cardiovascular events 30% more accurately than BMI alone.
Actionable Strategies for a Healthy BMI in 2026
Implement these five evidence-based tactics to achieve and sustain a healthy body composition:
BMI is a screening tool, not a diagnostic. Relying solely on it misses 25% of cases. Combine it with waist circumference and body fat percentage for a complete picture. A study in Obesity found waist-to-height ratio predicts cardiovascular risk 30% better than BMI alone.
Tips to Maintain a Healthy BMI
Here are 5 practical tips to reach and sustain a healthy BMI through nutrition and lifestyle:
- Exercise regularly – Aim for 150 minutes per week of moderate activity like brisk walking or biking. This helps burn calories and build metabolism-boosting muscle.
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains – These foods provide vitamins, minerals, fiber and volume to keep you full on fewer calories.
- Watch portion sizes – Use smaller plates and stop eating when you feel satisfied, not stuffed. This simple visual cue can reduce calorie intake by up to 22%.
- Cut added sugar and saturated fat. The American Heart Association’s 2026 guidelines recommend under 24g of added sugar daily. Limit saturated fats to under 7% of total calories to improve cardiovascular biomarkers.
- Weigh yourself weekly – Consistent monitoring helps you identify trends. Modern smart scales like the Withings Body Comp sync data directly to health apps for trend analysis.
Person standing on scale
Reaching a healthy BMI requires consistent action. Use this guide as your foundation and track your progress with tools like the MyFitnessPal app.
What is a healthy BMI range?
Person standing on scale
Making lifestyle changes to reach a healthy BMI takes dedication, but it is worth it! Use this guide to understand BMI and take steps towards improving your health.
What is a healthy BMI range?

A healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) for adults in 2026 is 18.5 to 24.9. This range correlates with the lowest statistical risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
A BMI below 18.5 is classified as underweight. A reading of 25 to 29.9 indicates overweight, while 30 or higher defines obesity. Health risks escalate proportionally with increasing BMI.
BMI remains a population-level screening tool, not a diagnostic measure. It does not differentiate between fat mass, lean muscle—like that of an elite athlete—bone density, or account for age, sex, or ethnic variations. Consequently, it can misclassify muscular individuals or older adults.
Maintaining a BMI within the 18.5–24.9 range is a supportive pillar for metabolic health. For a complete picture, track your BMI trend alongside metrics like waist circumference and body composition scans from devices like the InBody 570.
Consult a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian if your BMI falls outside the standard range. They perform a comprehensive risk assessment and can develop a personalized nutrition and exercise strategy.
What are the specific health risks of an elevated or low BMI?
Maintaining a Body Mass Index (BMI) above 25 significantly elevates the risk for numerous chronic health conditions, including:
– Cardiovascular disease and stroke
– Type 2 diabetes
– Specific cancers, including breast and colorectal
– Hypertension
– Hypercholesterolemia
– Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD)
– Chronic kidney disease
– Osteoarthritis
– Obstructive sleep apnea
– Depression and anxiety disorders
The higher the BMI, the greater the risks. People with severe obesity (BMI over 40) face the most elevated risks. Even being just moderately overweight increases risks for conditions like heart disease significantly.
Being underweight (BMI below 18.5) also has health risks, including nutritional deficiencies, osteoporosis, decreased immunity, and issues with menstruation or fertility.
Maintaining a BMI in the healthy range of 18.5-24.9 can help minimize obesity-related health risks. But BMI has some limitations, so waist circumference and other health markers should also be considered for risk assessment.
Losing just 5-10% of body weight for those overweight/obese can already provide health benefits like improved cholesterol levels. Further, improving risks is often achieved with more significant weight loss. Likewise, gaining some weight for those underweight can help minimize risks related to low BMI.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a normal or healthy BMI range?
A healthy BMI range is typically between 18.5 and 24.9. This range is associated with the lowest risk for developing chronic diseases related to weight. If your BMI falls within this bracket, it generally indicates you have a healthy weight for your height according to this screening tool.
How do I calculate my BMI manually?
To calculate BMI manually, use the formula: BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]². For example, if you weigh 68 kg and are 1.75 meters tall, your BMI is 68 / (1.75 * 1.75) = 22.2. You can also use online calculators or BMI charts for a quicker assessment without the math.
Why is BMI important for my health?
BMI is important as a screening tool to assess your risk for obesity-related diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. It helps guide weight management decisions, indicating if you need to gain or lose weight, and allows you to track progress over time towards a healthier range.
What are the different BMI categories?
What are the limitations of using BMI?
BMI does not distinguish between muscle and fat, so it may misclassify very muscular individuals as overweight. It also doesn’t account for fat distribution (like visceral fat). Therefore, BMI should be used alongside other health assessments for a more complete picture of your health.
How can I find out my BMI if I use pounds and feet?
For imperial units (pounds and feet/inches), use the formula: BMI = [weight (lbs) / height (inches)²] x 703. Alternatively, most online BMI calculators allow you to input your measurements in either metric or imperial units to get your score and category instantly.
Conclusion
Your BMI is one health metric. Use it correctly.
Additional Resources
- CDC Website on BMI
- Examine.com – What is BMI?
- How useful is BMI? – Harvard Health
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/BMI/bmicalc.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/downloads/bmiforpactitioners.pdf
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/index.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000348.htm
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/index.html
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323543
- https://reverehealth.com/live-better/tips-to-maintain-a-healthy-weight/
- https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/assessing/bmi/adult_bmi/index.html
