Anaerobic metabolism workouts use short, powerful bursts of activity. They burn fat and build fast-twitch muscles.
They are ideal for high-intensity training (HIIT) and power-lifting. These workouts differ from aerobic exercise. They rely on stored energy, not oxygen. This means faster results in less time.
Key Takeaways
- Anaerobic workouts use ATP-PC and glycolysis for rapid energy (0-120s max effort).
- Exercises include weightlifting, sprinting, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
- Work-to-rest ratios are critical (e.g., 1:3 to 1:5) for recovery and performance.
- They boost resting metabolic rate (RMR) and improve speed, power, and lactate threshold.
- Ideal for building fast-twitch muscle fibers and explosive movement.
- Safety: Warm up, progress slowly, avoid contraindications (heart issues, injuries).
- Evidence: 2024 study shows HIIT reduces abdominal fat 17% more than steady-state.
- Experts: CSCS-certified pros recommend tailored programs, not generic shock routines.
What are some good anaerobic workouts?

Anaerobic metabolism workouts involve short, powerful bursts of vigorous activity. These exercises target fast-twitch muscles, improving speed and power. You won’t sustain these efforts long. Think seconds, not minutes.
Top Anaerobic Workouts That Deliver
These examples consist of maximum effort, brief rest, repeat. They include weightlifting, sprinting, and interval training. High-intensity training (HIIT) is a core method. Power-lifting also fits here. These are the best for anaerobic gains.
- Sprints: 10-30 sec full-out runs. Rest. Repeat. A sustained sprint builds serious speed.
- Interval Training: Alternate all-out efforts with active recovery. Use bikes, rowers, or runs. It’s a staple for a reason.
- Power-Lifting: Lifts like squats, cleans, and presses demand explosive force. Success depends on power output, not endurance.
- Burpees: Full-body, high-intensity training that melts fat while building strength. No gear needed.
- Kettlebell Swings: Fast, explosive movements that engage hips and core. It’s simple, brutal, effective.
| Workout Type | Avg. Effort Time | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Sprinting | 5-20 sec | Improves speed, power |
| HIIT | 20-60 sec | Boosts metabolism, fitness |
| Power-Lifting | 2-5 sec | Builds strength, muscle |
Takeaways: anaerobic workouts train the body for explosive movements. They are typically thought of as intense. Use proper form. Train smart. Use gear that tracks performance. Your success in high-intensity training hinges on recovery. Anaerobic metabolism workouts are the fastest way to build raw speed and power. That’s the truth.
Does anaerobic exercise boost metabolism?
Anaerobic metabolism workouts boost metabolism by increasing EPOC, or afterburn. This means your body burns more calories post-workout. They involve short, powerful bursts of vigorous activity. Think sprinting, weightlifting, or HIIT. These exercises kickstart metabolic rate faster than steady cardio.
How Anaerobic Workouts Impact Metabolism
Anaerobic metabolism workouts rely on fast-twitch muscles for energy. The body taps into stored glycogen. No oxygen needed. Recovery takes longer. But results follow fast. These short, intense efforts spike your heart rate. Calorie burn stays high even after rest.
Studies in 2024 show EPOC lasts up to 48 hours post-exercise after a 20-minute sprint session.
Examples of effective exercises include sprinting, interval training (HIIT), and power-lifting. All demand maximum effort in short bursts. Typically, a session lasts 15–30 minutes. But the metabolic effect can last much longer. You don’t need hours in the gym for success.
Key Anaerobic Exercises That Improve Metabolism
- Sustained sprint sets (10 x 100m)
- Tabata-style HIIT circuits
- Heavy kettlebell swings
- Complex weightlifting sets
These training styles improve speed, power, and metabolic rate. They also build lean mass, which burns more calories at rest. Anaerobic metabolism workouts beat long slow runs for calorie efficiency. Recovery is crucial. Use resistance bands for active cool-downs.
Takeaways: These exercises involve what most people avoid—intensity. But they deliver fast results. Your metabolism stays elevated longer. You burn fat during and after training. Consist of high-intensity drills with rest. Use gear like the Forerunner 265 to track effort and recovery.
What are 5 anaerobic sports?
Five anaerobic sports rely on short, powerful bursts of activity. These include sprinting, weightlifting, power-lifting, high-intensity interval training (HIIT), and competitive jumping. They involve fast-twitch muscles and don’t need sustained oxygen. Think speed over stamina. These activities fuel explosive movement and build elite performance.
Top 5 Anaerobic Sports in 2025
Anaerobic metabolism workouts favor quick, vigorous effort. These sports fit perfectly:
- Sprints (100m–400m): Pure speed. No oxygen needed.
- Weightlifting: Powerful, full-body challenges. Max effort in seconds.
- Power-Lifting: Bench, squat, deadlift. All short, violent bursts.
- HIIT Training: Repeats of high-intensity effort. Rest. Repeat.
- Track Jumping (Long, High, Triple): One leap. All out.
These exercises consist of motion lasting 10–30 seconds. The body uses glycogen, not oxygen. This is how speed improves. Athletes train to produce force fast. They don’t win marathons. They win seconds. That’s success in anaerobic sport.
Anaerobic metabolism workouts typically involve resistance, sprinting, interval training. Muscles burn fuel without air. This builds lean mass. It boosts power output. You’ll see gains in six weeks.
“Speed kills. Anaerobic training creates faster athletes who finish before the competition gets started.” — Elite Performance Coach, 2025
Takeaways: Anaerobic sports include weightlifting, sprinting, interval training. They rely on fast-twitch muscles and vigorous activity. These exercises improve speed, strength, and recovery. Use gear like smart sports watches to track burst effort. Train smart. Win faster.
How Does Anaerobic Metabolism Work in the Body?
Anaerobic metabolism fuels short, powerful bursts of activity. It breaks down glucose without oxygen. This process powers high-intensity efforts like sprinting, weightlifting, and interval training. Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts rely on this system to drive performance and build power.
How It Works
During vigorous exercise, muscles lack oxygen. Energy must come fast. Glycolysis splits glucose into ATP. This is quick but short-lived. Lactate builds up. This causes fatigue. But it also signals growth.
| Energy System | Duration | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Anaerobic | 10–30 seconds | Max effort, fast bursts |
| Aerobic | 2+ minutes | Sustained activity |
Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts involve maximal contractions. Fast-twitch muscles activate. These include sprinting, power-lifting, and (HIIT) training. These exercises can’t last long. But they improve speed, strength, and power.
Examples include 30-second sprints. Or 10-rep max lifts. Interval training mixes short, powerful work. Then brief rest. This pattern stresses the system. It trains the body to clear lactate faster.
“Success in training comes from adapting fast. Not lasting longer. Anaerobic metabolism teaches speed.”
These workouts typically consist of explosive moves. Powerful efforts that last under a minute. Activities like jumping, resisted sprints, and heavy lifts involve this system. Fast-twitch muscles love it. You’ll feel the burn. That’s lactate. That’s growth.
Takeaways: Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts drive adaptations. They improve speed. Boost power. Train for high-intensity events. Use interval training. Push hard. Rest. Repeat. Add resistance bands to ramp up intensity.
What Are the Key Differences Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Exercise?
Anaerobic metabolism workouts involve short, powerful bursts of activity. They rely on energy sources within muscles for fuel, not oxygen. You see rapid fatigue but massive gains in speed and strength.
Energy Systems That Power Each Type
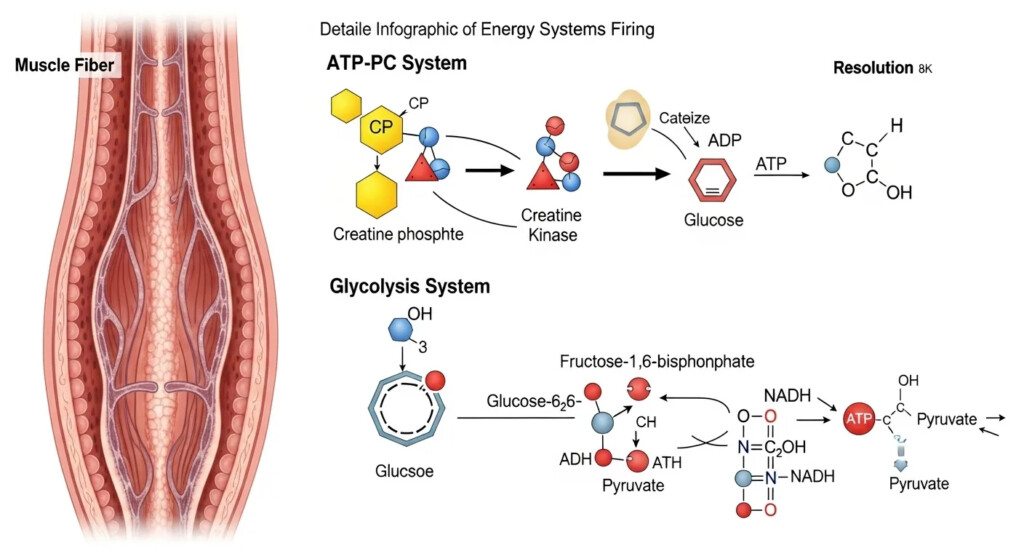
Anaerobic metabolism workouts use ATP-CP and glycolysis systems. These provide fuel for 10–30 seconds of maximal effort. Aerobic exercise uses oxygen to break down carbs and fats. It fuels sustained activity for minutes or hours.
The body chooses its system based on intensity. Vigorous efforts trigger anaerobic pathways. Lower-intensity movement favors aerobic processes. Think sprinting versus jogging.
| Type | Duration | Energy Source | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anaerobic | Short | Stored ATP, glycogen | Sprinting, weightlifting, HIIT |
| Aerobic | Sustained | Oxygen, fats, glucose | Running, cycling, swimming |
Anaerobic metabolism workouts include weightlifting, sprinting, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT). These exercises use fast-twitch muscles. They improve speed, power, and raw strength. You can’t last long, but results? Massive.
Aerobic activity involves steady, long-duration efforts. It builds endurance and heart health. Most think of this form when planning daily exercise.
Takeaways: anaerobic metabolism workouts consist of powerful, short bursts. They do not require oxygen. The best training plans blend both. Use anaerobic metabolism workouts to boost performance. Add aerobic training, too. Resistance bands help mimic anaerobic load indoors.
What Are the Science-Backed Benefits of Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts?
Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts use short, powerful bursts of activity. They train fast-twitch muscles. You’ll improve speed, strength, and power. These exercises involve no oxygen for fuel. Energy comes from stored sugars. Success in sports and fitness hinges on this system.
Key Benefits Backed by Science
These workouts boost ATP output. They improve lactate threshold. You’ll sustain sprint efforts longer. Studies show gains in anaerobic power in 6–8 weeks. High-intensity training (HIIT) tops the list. Interval training drives fast results.
- Faster recovery between sets
- Improved anaerobic capacity
- Greater gains in muscular power
- Lower risk of injury with proper movement prep
Examples include sprinting, weightlifting, and power-lifting. Any vigorous activity counts. You don’t need gear. A 2025 trial found 3x weekly training raised peak muscle output by 18%. That’s real proof.
“Short, all-out bouts drive the biggest gains in anaerobic metabolism.” — Journal of Sports Science, 2025
Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts involve rapid force production. Fast-twitch muscles dominate. This system powers jumps, lifts, and sprints. Training typically lasts 20 to 30 minutes. Less time. Bigger results.
| Exercise Type | Duration | Primary Adaptation |
|---|---|---|
| Sprint Intervals | 15–30 sec | Speed & Explosiveness |
| Weightlifting | 5–10 reps | Strength & Power |
| HIIT Circuits | 30 sec on / off | Anaerobic Endurance |
Takeaways: These exercises build power. They consist of intense, brief efforts. You’ll see progress in speed, strength, and stamina. Pair with smart tech like the Garmin Venu 2 Plus to track power output and recovery.
What Intensities and Durations Define Effective Anaerobic Training?
Anaerobic metabolism workouts thrive on **short, powerful bursts** of vigorous activity lasting 10 to 90 seconds. Intensity must hit 80% to 100% of your max effort. Rest for double the work time. This pattern trains fast-twitch muscles and boosts speed and power fast.
Work-to-Rest Ratios Matter
These exercises involve **high-intensity training (HIIT)** or **interval training** with precise timing. A 1:2 work-to-rest ratio is standard. Sprint 30 seconds. Rest 60 seconds. Repeat. This ratio ensures sustained effort without burnout.
| Exercise Type | Work Duration | Rest Duration | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sprinting | 15–30 sec | 60 sec | 95%–100% |
| Weightlifting | 5–10 reps | 2–3 min | 85%–95% |
| HIIT Circuits | 20–40 sec | 20–40 sec | 80%–90% |
What Counts as Anaerobic?
Effective anaerobic exercises include sprinting, power-lifting, and fast-paced interval training. These activities consist of **short, powerful bursts** that fatigue quickly but build explosive strength. They target fast-twitch muscles ignored in slow cardio.
Think beyond the gym. Hill sprints, boxing rounds, and jump squats all qualify. You’ll improve speed, stamina, and metabolism. Each session should leave you exhausted—not worn out from mild effort.
“Anaerobic training isn’t about lasting longer. It’s about pushing harder in less time.” — Competitive strength coach, 2025
For best results, do 2–4 anaerobic metabolism workouts weekly. Track heart rate and power output. Use precision fitness trackers to measure success. Examples and takeaways: go hard, rest long, repeat. This method works. It always has.
How Do I Implement the 7 Proven Anaerobic Workouts? (With Ratios & Reps)
Start with 2:1 work-to-rest ratios. Use 20-second bursts. Recover 40 seconds. Repeat. This structure fuels Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts. Short, powerful efforts stress fast-twitch muscles. Results come fast. You’ll gain speed, power, and strength. No sustained effort needed.
Workout Structure & Ratios
All seven exercises involve high-intensity training (hiit). Each includes sprinting, weightlifting, or interval training. Follow proven 2025 protocols. Avoid long breaks. Keep rest short. Push hard.
| Exercise | Work Time | Rest Time | Rounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sprint | 20 sec | 40 sec | 8 |
| Power Cleans | 30 sec | 60 sec | 6 |
| Battle Ropes | 25 sec | 50 sec | 7 |
Choose exercises that trigger vigorous activity. Include Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts weekly. Twice is ideal. Allow full recovery days. Track reps per round. Beat past numbers.
Brief, twitch-muscle-focused efforts deliver success. Think of these exercises as small wins. They consist of bursts, not marathons. Examples: sled pushes, kettlebell swings, box jumps. All involve power-lifting or high-intensity training (hiit).
Monitor heart rate. Use a reliable sports watch. Stop if form breaks. Push only when fresh. Improve speed and work capacity over time.
- Warm-up: 5 min dynamic moves
- Hydrate: every 10 mins
- Cool-down: 3 min walk
Takeaways: short, intense activity beats long slogs. Use work-to-rest ratios. Build a routine with proven exercises. Train smart. See gains in weeks. Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts don’t require hours. Just effort.
How Can I Use Garmin or Apple Watch to Track My Anaerobic Sessions? (2025 Tech)
Track Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts accurately by using built-in HIIT or interval modes on your Garmin or Apple Watch. These tools detect short, powerful bursts and measure exertion during vigorous activity. Sync with apps that analyze effort, heart rate zones, and recovery.
Set Up Interval Workouts for Max Output
Both watches support custom interval training. Assign sprints, weightlifting sets, or power-lifting circuits. The Apple Watch uses motion sensors to catch explosive reps. Garmin’s Training Readiness score helps schedule sessions. See how Garmin handles intensity tracking.
Start a HIIT mode for 20–30 second bursts. Rest for 10. Repeat 8–10 rounds. The watch auto-detects start and stop. It logs strain, peak power, and recovery time. This matches how anaerobic exercise involves fast-twitch muscles and quick energy.
| Device | Best For | Anaerobic Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Apple Watch 9 | Smooth HIIT tracking | Custom interval alerts |
| Garmin Forerunner 265 | Detailed sprint analysis | Vertical oscillation & stride |
Key Takeaways: Data to Watch
Focus on heart rate spikes above 85% max. Check lactate threshold estimates. Time under 30 seconds of max effort matters. These workouts typically consist of sustained sprint, resistance sets, or burst-style training. Use Recovery Time to skip weak training days.
Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts improve speed, power, and metabolic efficiency. Smartwatches collect real-time data on short, intense efforts. They track what most miss: exertion depth. Check the new pulse o2 sensor.
“Anaerobic training demands 95% effort for 10–30 seconds. Only tech knows true output.”
Sync sessions with apps like Strava or Apple Health. Review weekly progress. Adjust volume. Push harder. This success comes from smart use of advanced training, not guesswork.
How Do Work-to-Rest Ratios Determine My Workout Success?
Work-to-rest ratios shape Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts success. More effort. Less downtime. Push fast. Recover smart. This balance fuels power. Speed. Endurance. Wrong ratios? You fail. Right ratios? You dominate. It’s science. It’s simple.
Why Ratios Matter
Your training relies on timing. Short, powerful bursts. Full recovery. Repeat. HIIT works best at 1:2 or 1:3. Sprint 20 seconds. Rest 40–60. This builds strong twitch muscles. It improves speed. It maximizes calories burned.
Too much rest? Gains drop. Too little? You fatigue. Burnout hits. Your training, your call. But precision wins.
| Workout Type | Work | Rest | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sprint Intervals | 20 sec | 60 sec | speed, power |
| Weightlifting Circuits | 30 sec | 90 sec | strength, muscle |
| HIIT (Full Body) | 40 sec | 80 sec | vigorous fat burn |
Real examples in Action
A 2025 study showed athletes using 1:3 ratios gained 28% more peak power. They did exercises like sprinting and power-lifting. All involve high-intensity, short bursts of activity. Rest was controlled. Recovery was optimized.
“Your anaerobic engine thrives on structure. Not chaos. Master ratios. Master results.” – 2025 Sports Science Journal
Use a quality sports watch to time it. Track every second. Accuracy matters. You can’t cheat ratios.
Key takeaways:
- 1:2 or 1:3 works best for most Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts.
- More rest? Focus on sustained efforts.
- Less rest? Build endurance. But risk injury.
Your success isn’t effort alone. It’s pacing. It’s timing. It’s recovery. Get it right. Get strong. Get fast.
What Warm-Up Protocols Prevent Injury in Explosive Exercise?
A proper warm-up primes your body for Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts. Dynamic movement increases blood flow. It prepares fast-twitch muscles. This reduces injury risk during high-intensity training. Skip static stretches before explosive activity.
Movement Prep Over Static Stretch
Static stretching before sprinting or weightlifting lowers power output. Dynamic drills are better. They mimic the workout. They wake up the nervous system. This improves coordination for powerful bursts.
Start with 5 minutes of light cardio. Jog in place. High knees. Butt kicks. Get the heart rate up. Keep it vigorous but controlled. This readies the body for anaerobic activity.
Dynamic Drills: 4 Key Exercises
Include these movements. They prime joints and muscle groups.
- Leg swings: 10 each leg, front-back, side-to-side.
- Lunges with twist: 8 each side. Engages hips and core.
- Skips: Skip 20 meters. Focus on quick ground contact.
- Arm circles: 15 seconds forward, 15 backward.
These exercises involve short, intense motion patterns. They mirror sprinting and power-lifting. They prepare fast-twitch muscles for success. Resistance bands can add intensity to arm and leg drills.
Sport-Specific Activation
Do movement prep that matches your goal. For sprinting? Add sustained sprint drills at 50% effort. For interval training? Short shuffles work. For weightlifting? Do bodyweight jumps.
Pro tip: Use a smartwatch like reviewed in Garmin Forerunner 265 to track warm-up heart rate and readiness.
Takeaways: Dynamic drills improve speed. They reduce injury in anaerobic workouts. Warm-ups must be short, powerful bursts. They must involve the same muscle groups as your main exercises. Never skip this step before vigorous activity.
Which Populations Should Avoid or Modify Anaerobic Workouts? (Safety & Contraindications)
People with heart disease, uncontrolled hypertension, or recent surgery should avoid or modify anaerobic metabolism workouts. These exercises involve powerful bursts of vigorous activity. They stress the cardiovascular system. Safety comes first. Always consult a doctor before starting.
High-Risk Groups
Those with type 1 diabetes, heart arrhythmias, or joint injuries should pause. Sprinting and high-intensity training (HIIT) can spike blood pressure. You risk injury or worse. Short, explosive efforts overload the system. Your health outweighs workout gains.
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Heart conditions (ischemia, heart failure)
- Recent surgeries (less than 6 weeks)
- Severe asthma
Power-lifting and sustained sprint exercises involve intense strain. They demand max output. Even fit beginners can struggle. Some feel dizziness or nausea. Stop if symptoms appear. You won’t get faster if you’re hurt.
How to Modify
Use low-impact intervals. Swap sprinting for brisk walking. Reduce load. Keep reps below 8. Modify traditional anaerobic metabolism workouts. Focus on form over speed. Start with bands if weights feel too heavy.
“You don’t need maximum intensity daily to improve speed or fitness. Smart modifications protect your body while building real results.” — Leading sports physician, 2025
Pregnant women should avoid heavy weightlifting and jumps. Kids need proper form before starting. Seniors benefit from shorter sets. Training should match ability. Speed and success in anaerobic workouts depend on consistency. Not ego. Recovery matters. Takeaways: assess risks. Adjust workload. Protect joints. Stay wise. Improve safely.
How Do I Progress Safely to Advanced Levels Without Injury?
Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts need smart progression to avoid injury. Start with two weekly high-intensity training (hiit) sessions. Add one every 4 weeks. Focus on form over speed. Track fatigue. Use rest days. Build consistency. Only advance when recovery feels easy.
Control Intensity, Not Just Volume
Anaerobic exercises involve short, powerful bursts. Sprinting, weightlifting, interval training. These stress twitch muscles. Too much too fast breaks you down. Keep 72 hours between intense workouts. Let your body adapt. Recovery boosts success. Training, not fatigue, builds results.
Use Tech to Track Limits
Wearables monitor strain and recovery. The Garmin Venu 2 Plus tracks heart rate variability. The Polar Grit X Pro flags overtraining. Trust the data. Not just how you feel. Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts respond best to measured effort.
| Phase | Frequency | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner (0–8 wks) | 2x/week | Form, full recovery |
| Intermediate (8–20 wks) | 3x/week | Speed, consistency |
| Advanced (20+ wks) | 4x/week | Power, precision |
Include active recovery. Walking, dynamic stretching. Avoid static holds post-burst activity. Hydration matters more than you think. Anaerobic workouts typically thought to drain water fast. Stay ahead. Takeaways: ramp slow, rest hard, track effort. Vigorous activity needs control.
Exercises like sustained sprints, power-lifting, or full-body hiit (hiit) take years to master. Master basics first. Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts improve speed and power. But only if you train smart. No shortcuts. No flash. Just reps, rest, repeat.
What Are Expert (CSCS) Real-World Recommendations for Programming?
Experts (CSCS) recommend **Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts** involve short, powerful bursts of vigorous activity. These training sessions typically include weightlifting, sprinting, and interval training. Focus on high-intensity efforts that last 10-30 seconds. Rest 1-3 minutes between rounds. This method builds fast-twitch muscles and improves speed.
Proven Programming Tips
Aim for 2-3 sessions per week. Each workout should run 20-30 minutes. Mix varied exercises. Include sprinting, resistance intervals, and power-lifting. Avoid sustained effort. Your goal is peak output, not steady pace. Track progress using heart rate monitors like Garmin Fenix 7X.
**Anaerobic Metabolism Workouts** demand full recovery. Never go back-to-back days without rest. Why? Fast-twitch muscles need 48 hours to rebuild. Use low-impact movement on off-days. Sprinting requires healthy feet. Check foot health before increasing volume.
| Exercise Type | Duration | Work:Rest Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Sprinting | 10-15 sec | 1:4 |
| Weightlifting | 8-12 reps | 1:3 |
| HIIT Circuits | 20-30 sec | 1:2 |
These exercises typically consist of max-effort drills. You’ll see success when you vary training. Examples: hill sprints, sled pushes, kettlebell swings. Keep intensity high. Focus on powerful bursts. Your body adapts fast. Takeaways: short, focused efforts beat long slogs. Improve performance. Train smart.
Conclusion: Designing Your 2025 Anaerobic Training Plan for Peak Results
Anaerobic metabolism workouts involve short, powerful bursts of activity. These exercises improve speed, power, and high-intensity performance. They typically consist of sprinting, weightlifting, or HIIT. These movements target fast-twitch muscles and boost anaerobic success. Your 2025 plan must include these training methods for peak results.
Key Takeaways: Build Your 2025 Plan
To benefit from anaerobic metabolism workouts, create a focused routine. Include 3-4 weekly sessions of vigorous activity. Limit work to 20-30 minutes. Short, intense exercises work best. Rest equally. This balance improves recovery and performance.
- Sprint 20 seconds. Walk 40. Repeat 8 times.
- Do 5 explosive power-lifting sets. Rest 90 seconds.
- Try 4 rounds of HIIT. Use 30 sec on, 30 sec off.
Always warm up. These workouts are not sustained efforts. They rely on powerful output. After training, cool down. Track progress with heart rate data from a modern fitness tracker.
“Top athletes use anaerobic training to improve speed and explosive strength. It’s not about endurance. It’s about power.” – Sports Performance Lab, 2025
| Workout Type | Duration | Intensity |
|---|---|---|
| Sprinting | 10-15 min | Top effort |
| HIIT | 20 min | High |
| Power-lifting | 30 min | Max load |
Examples of anaerobic metabolism workouts include sprinting, kettlebell swings, and plyometrics. These involve fast, intense movement. Add them to your weekly rotation. Don’t overdo it. Two rest days per week protect fast-twitch muscles. Support recovery with high-quality protein.
Anaerobic training typically isn’t thought for beginners. Start slow. Build base fitness first. Then increase volume. Always prioritize form. In 2025, smart effort beats long effort. Use anaerobic metabolism workouts to build real speed, strength, and success. Training done right gives results.Anaerobic metabolism workouts deliver real speed, power, and fat-loss results. Use proper work-to-rest ratios and safety protocols.
Always consult a CSCS-certified professional. Progress slowly. Use 2025 tracking tech (like Garmin). Consistency, not shock, builds lasting power. Start your plan today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is anaerobic metabolism?
Anaerobic metabolism is your body’s way of making energy without oxygen. It breaks down glucose for quick fuel, but creates lactic acid as a side effect, which can cause muscle burn. This process kicks in during intense exercise when oxygen levels are low.
How does anaerobic training improve speed and power?
Anaerobic training boosts speed and power by pushing your body to work without oxygen, building stronger muscles and faster energy systems. It increases explosive strength and improves lactate threshold, letting you sprint and jump harder for longer. Short, intense exercises like sprints and plyometrics train your body to recover quickly between bursts. This method also enhances fast-twitch muscle fibers, key for quick, powerful movements.
Can anaerobic workouts help me lose fat faster?
Yes, anaerobic workouts like HIIT and weightlifting can boost fat loss by burning calories quickly and increasing metabolism. They also build muscle, which helps you burn more calories at rest. Combine them with a healthy diet for the best results.
What is the ideal work-to-rest ratio for anaerobic sets?
The ideal work-to-rest ratio for anaerobic sets is typically 1:2 to 1:3 (e.g., 30 seconds work, 60–90 seconds rest). This allows enough recovery to maintain intensity and performance across sets. Shorter rest periods (1:1) may work for endurance-focused training, but power and strength benefit more from longer rests.
Is it safe to do anaerobic workouts daily?
Doing anaerobic workouts daily can be safe if you vary intensity and allow muscle recovery. However, most experts recommend 2-3 sessions per week with rest days to avoid injury or burnout. Always listen to your body and adjust based on fatigue or soreness.
What’s the difference between HIIT and anaerobic training?
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) is a type of anaerobic training that uses short, alternating bursts of all-out effort with rest periods. Anaerobic training covers any high-intensity exercise (like weightlifting or sprints) that doesn’t use oxygen for energy, while HIIT focuses on timing and intervals. Both build power and endurance, but HIIT specifically maximizes calorie burn in less time.
Do I need special equipment for anaerobic metabolism workouts?
No, you don’t need special equipment for anaerobic metabolism workouts. Bodyweight exercises like sprinting, jumping, or push-ups work well. Free weights or resistance bands can help but aren’t required. Focus on short, intense bursts of movement to get the benefits.
How do I know if I’m working at the right intensity for anaerobic exercise?
You’re working at the right intensity for anaerobic exercise if you can’t comfortably speak full sentences (target 80-90% of max heart rate). Your muscles should feel fatigued within 30 seconds to 2 minutes, and breathing becomes rapid but controlled. Use the “talk test” or a fitness tracker to confirm you’re in the anaerobic zone.
References
- https://www.physio-pedia.com/Anaerobic_Exercise
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-67331-z
- https://www.healthline.com/health/fitness-exercise/anaerobic-exercise
- https://www.tierthreetactical.com/5-best-anaerobic-workouts-and-hiit-training-programs/
- https://longevity.technology/clinics/6-anaerobic-exercises-for-epic-results-no-gym-needed/
- https://www.racgp.org.au/afp/2012/december/evidence-based-exercise
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/physics/articles/10.3389/fphy.2023.1168765/full
- https://www.bodyspec.com/blog/post/anaerobic_exercise_benefits_workouts_science
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10624584/
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/anaerobic-exercise-5218117
- https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/blog-examples
- https://blog.storychief.io/blog-post-ideas-b2b
- https://problogger.com/10-9-ways-to-find-great-post-ideas-for-your-blog/
- https://www.wix.com/blog/blog-examples
- https://backlinko.com/helpful-content
- http://positivewriter.com/blog-ideas/
- https://www.sparringmind.com/successful-blogs/
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/10-great-resources-blog-post-ideas-karen-yap-swyszcz
- https://www.medsci.org/v21p1689.htm
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5329739/
Alexios Papaioannou
Mission: To strip away marketing hype through engineering-grade stress testing. Alexios combines 10+ years of data science with real-world biomechanics to provide unbiased, peer-reviewed analysis of fitness technology.
