What is the Role of Glycogen, and what does it do for your body? Why is it so important to exercise physiology? What are the side effects of insufficient glycogen in your system, and how can you get more? This article will provide an overview of what this critical substance does for our bodies.
Introduction
When your body requires energy, it can use its glycogen stores. The molecules made from sugar in your food are primarily kept in your liver and muscles. Your body can promptly activate glycogen from these storage sites when it requires fuel.
What you eat, how you usually eat, and your activity level influence how your body stores and utilizes glycogen. Low-carb as well as ketogenic diets, as well as strenuous exercise, diminish glycogen stores, causing the body to shed fat for energy.
The body breaks down most carbs from our foods and transforms them into sugar. Sugar is the primary source of fuel for our cells. When the body doesn’t need to utilize the sugar for power, it saves it in the liver and muscles. This kind of glucose is made up of several connected glucose particles and also is called glycogen. When the body needs a quick increase of energy or isn’t obtaining sugar from food, glycogen is damaged to release glucose into the bloodstream to be utilized as gas for the cells.
Key Takeaways
- Glycogen is stored mainly in the liver and muscles.
- It provides immediate energy during physical activities.
- When dietary carbohydrates are low, the body breaks down glycogen for energy.
- Glycogen also plays a critical role in brain function by maintaining necessary glucose levels.
What is the Role of Glycogen?
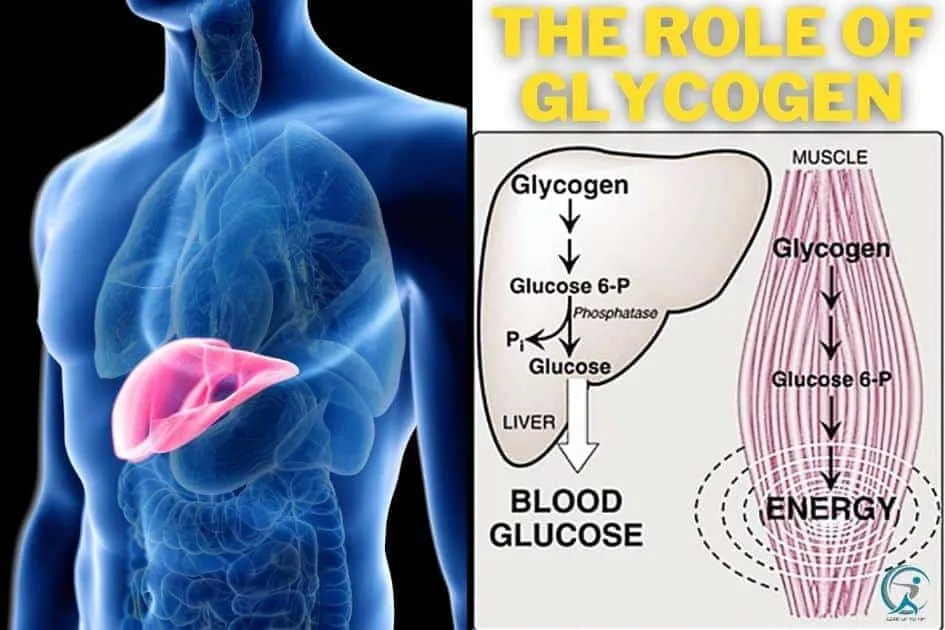
Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose that works as a form of animal power storage. The polysaccharide framework of sugar shows the primary storage space form of sugar in the body.
Our bodies need the energy to survive and keep going, but we also need the proper nutrients. Glycogen is a carbohydrate that’s stored in our livers and muscles. It’s how our bodies create glucose for this exact purpose. The more strenuous the day we have, the more glycogen that gets burnt up. Like how a car doesn’t run without fuel – and since fuel creates energy, we call glycogen the body’s primary energy source!
Glycogen: The Body’s Energy Reserve
Glycogen, stored mainly in the liver and skeletal muscle cells, plays a pivotal role in maintaining blood glucose levels, particularly under physiological conditions that demand a quick energy source, such as during moderate-intensity or prolonged exercise.
The rate of glycogen synthesis is directly proportional to the amount of dietary carbohydrates consumed, with fruits being a rich source. According to a study by Jensen et al., a high-CHO diet can significantly elevate muscle glycogen levels compared to a low-CHO diet.
Glycogen Breakdown: Providing Energy When Needed
Without dietary carbohydrates, the body resorts to glycogen breakdown to sustain energy. The glycogen branching enzyme facilitates the transformation of glycogen into glucose, which subsequently enters the bloodstream to raise blood glucose concentrations.
However, under extended periods of low-CHO diet or in pathological conditions like glycogen storage disease – where the glycogen branching enzyme is defective – the breakdown of glycogen becomes an absolute requirement. In these scenarios, fatty acids and amino acids are alternative energy sources.
Glycogen’s Role in Brain Function
Interestingly, glycogen’s role extends beyond muscle and liver tissues. Glial cells store glycogen in the brain, which is crucial for normal brain function. According to research published in Brain Res., the presence of glycogen in glial cells helps maintain the normal range of glucose needed for brain activities.
Additionally, under conditions requiring increased brain activity, the breakdown of glycogen becomes crucial. This highlights glycogen’s essential role in various tissues under various dietary and physiological conditions, reinforcing Claude Bernard’s initial discovery about glycogen’s pivotal role in energy homeostasis.
Glycogen is a storage space kind of sugar
The liver can store about a pound, and muscle glycogen stores can hold up to 2 kilograms, but excess body fat is the easiest to keep. This is because fats also help our bodies feel full and provide calories. Liver glycogen is an essential power resource for our brain, while muscle mass glycogen provides a prompt energy source during the workout.
The biggest concern with eating protein throughout and for an intense workout is that the blood circulation to your stomach is limited as it’s guided to the muscular tissues being worked. The energy you’re eating is not instantly available for those exercising body mass. That’s why it’s helpful for professional athletes to have big storage space.
We also know that the higher the workout intensity, the higher the energy section coming from glucose. For instance, at rest, as high as 70% of energy is derived from fat. However, when the optimum strength is reached, it is 100% sugar, not fat!
Glycogen and elite athletes
Elite athletes’ glycogen storage space dimension determines the intensity they can obtain. It’s no wonder why Michael Phelps switched to an extremely high-carb diet, where around 75% of overall calories originated from carbohydrates while training. This is additionally the thinking behind why endurance athletes like to carb-load before a huge race.
According to the Biochemistry Primer for Workout Science (Michael Houston, Human Kinetics), the amount of glycogen you can keep is minimized to negligible to much less than fifty percent on a low carbohydrate diet. At the same time, it can be virtually doubled on a high-carb diet regimen. Nonetheless, consuming even more is insufficient. One must use it up by training to keep massive storage of glycogen.
As a result, if a person is lazy, a limited amount of glycogen is trivial; however, it makes a significant difference for a go-getter. This describes why some Kenyan runners can compete long without eating power beverages. Their storage space might be more extensive than American runners, that consume even more protein but not enough carbs and antioxidants from plant-based foods.
Structure of Glycogen
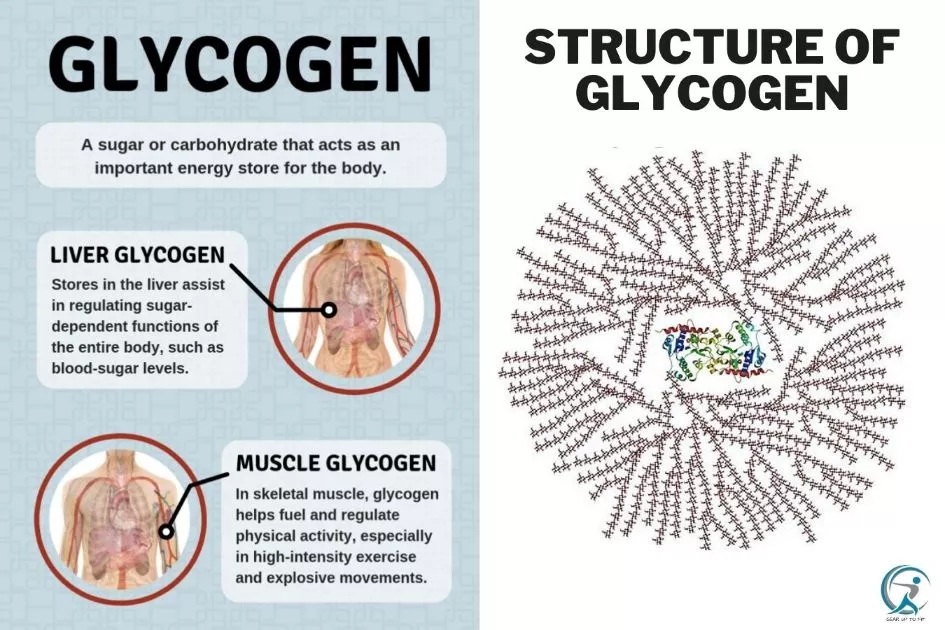
Glycogen comprises long polymer chains of sugar devices bonded with an alpha-acetal linkage—this acetal link combines the carbonyl group and the alcoholic team. Suppose the carbonyl group is an aldehyde team, i.e. (- CHO), and labeled as hemiacetal if there is a ketonic group. If 2 alkoxy teams adhere to the same carbon atom, it describes the acetal team.
So What is the Role of Glycogen?
Glycogen describes the analog of starch, a glucose polymer that operates as power storage in plants. It has a similar framework to amylopectin, a component of starch that is more extensively branched and compact than starch.
This polymer of glucose residues is connected by a -( 1,4) and a-( 1,6)- glycosidic bonds. It is discovered in the kind of granules in the cytoplasm in different cell types and plays an essential role in the glucose cycle. It creates a power get that can be quickly set in motion to satisfy sudden requirements for sugar.
Every glycogen granule has its core glycogen in protein due to the glycogen is synthesized. In muscles, liver, and fat cells, glycogen is kept in the hydrated type. It is composed of 3 to four components of water of glycogen that are associated with 0.45 millimoles of potassium per gram of glycogen.
Functions of Glycogen
Liver glycogen is a glucose reserve that hepatocytes launch when necessary to maintain regular blood glucose degrees. There is 40 kcal in body fluids, while hepatic glycogen can supply 600 kcal after a fasting night.
Sugar from glycogen stores continues to be within the cells in skeletal and cardiac muscle tissues and is also used as an energy source for muscle mass jobs.
Mind includes a percentage of glycogen in astrocytes. It gets collected throughout sleep and also is activated upon strolling. Glycogen reserves likewise assure a moderate degree of security versus hypoglycemia.

It was a specialized function in fetal lung type II lung cells. These cells build up glycogen at about 26 weeks of gestation and then manufacture lung surfactants.
Glycogen Manufacturing and Storage
Most carbs we consume are transformed into glucose, our primary energy source. When the body doesn’t require fuel, the sugar particles are linked in chains of eight to 12 sugar devices that create a glycogen molecule.
The primary trigger for this process is insulin. Your blood glucose degree will certainly increase when you consume a carbohydrate-containing dish. Increased glucose signals the pancreas to generate insulin, which helps the body take up sugar from the blood for energy.
Insulin instructs the liver cells to produce an enzyme, glycogen synthase, that connects sugar chains.
As long as sugar and insulin remain plentiful, glycogen particles can be provided to the liver, muscular tissue, and even fat cells for storage.
Glycogen composes around 6 percent of the liver’s total weight. Much less is saved in the muscle mass (only about 1 to 2 percent), which is why we lack power quickly throughout strenuous exercise.
Where does body store glycogen?
The quantity of glycogen saved in these cells can vary depending on how active you are, how much power you burn at the remainder and the types of food you consume. The muscles mostly utilize glycogen stored in the muscle, while those stored in the liver are distributed throughout the body – mainly to the mind and spine.
Glycogen should not be perplexed with the hormonal agent glucagon, which is also essential in metabolic carbohydrate rate and blood glucose control.
How Your Body Makes Use Of Glycogen?
At any offered time, there are about 4 grams of sugar in your blood. When the degree begins to decline – either because you have not consumed or are shedding sugar during a workout – insulin degrees will certainly also decrease.
When this occurs, an enzyme called glycogen phosphorylase starts damaging glycogen to provide the body with glucose. For the following eight to 12 hrs, glucose originating from liver glycogen is the body’s vital energy source.
How does your body store sugar for long activities?
To comprehend glycogen depletion, let’s first clarify how your body gets energy (glucose) for emergencies. To clue you into the value of sugar, the brain, and main nerve system use seventy-five percent of glycogen (kept glucose). It’s no surprise that we get hungry.
Glycogen is either formed directly from food (glycogen synthesis) or through an indirect path (gluconeogenesis). When you consume a meal with carbohydrates, your body launches insulin, which takes sugar from the blood for energy into the cells. The glucose particles are connected in a chain when the body obtains excess fuel, producing more extended glycogen units.
Glycogen has a max level of storage space before it obtains transformed into fat. Storage levels rely on your body and aspects such as task level, sex, and even muscle mass. Your body can store between 1,600-2,800 calories of carbohydrates in the type of glycogen in your muscular tissues, liver, red cell, and kidneys before it is transformed into fat.
Glycogen’s Impact on Athletes
Elite athletes recognize this factor well – their ability to push themselves largely depends on the size of their glycogen storage. Michael Phelps famously adopted a high-carb diet while training, where roughly 75% of total calories came from carbs! Endurance athletes similarly carb-load before major races to maximize their performance potential.
Your dietary habits also influence how much glycogen can be stored; reducing carbs intake can severely deplete these reserves, whereas adopting a high-carb diet can potentially double them!
How Does Your Body Use Glycogen?
Everyone has different capacities for storing glucose as glycogen – typically between 1,600-2,800 calories worth found across various organs, including muscles, liver, red blood cells, and kidneys, before it transforms into fat.
When our dietary intake fails to meet our glucose requirements or an intense workout uses up existing reserves – we tap into our stored glycogen stocks (a process known as ‘glycogenesis’). If these stocks get depleted entirely then fatigue sets in rapidly, alongside decrease in exercise performance levels.
Remember though that muscle-stored glycogens can only be utilized by those specific muscles where they are stored – they cannot relocate elsewhere within the body.
The duration taken to exhaust these stocks depend heavily on type and intensity level of workouts but on average:
- Regular daily activities use up these reserves within roughly 12-22 hours
- Low/moderate-intensity workouts take approximately 90-120 minutes
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) lasts around 20 minutes
But replenishment requires almost a full day after complete depletion!
Why Are Carbs Essential For Exercise?
A primary reason carbohydrates are so critical during periods of exercise lies in brain functionality. Even during rest periods – our brains use up more than half of bodily glucose supplies; throughout an average day, this represents nearly 20% of total bodily energy needs!
So what happens if following reduced carb dietary plans? Initial stages often lead to significant reductions in accumulated glycogens – leading to symptoms like fatigue or mental dullness until adjustments occur, allowing for renewed accumulation.
Understanding Glycogenesis
Most consumed carbs convert into glucose, which is the main source of bodily energy; whenever excess supplies exist beyond immediate needs – these combine, forming larger chains consisting of eight linked sugar units constructing single molecules termed ‘glycogens’.
Insulin produced by the pancreas plays a key role here – aiding uptake of sugars from the bloodstream towards energizing cellular activities while simultaneously signaling liver cells production enzyme named ‘glycogene synthase’ attaching along chains sugars together enabling continued supply provided both remain plentiful, thus permitting distribution among liver/muscle/fat cells situated optimally depending individual circumstances aligning specifically with current lifestyle choices (diet/exercise).
What is glycogen depletion?

When we do not have adequate sugar in our diet plan or use it throughout the workout, we take advantage of our body’s valuable books. The liver releases glycogen if your blood sugar levels drop (lower than average). Then glycogen is broken down so the glucose can be shared. This complex system, called glycogenolysis, assists in the equilibrium of blood glucose degrees. When all the glycogen is depleted, you will feel tired and tired, and your workout efficiency will experience.
The glycogen kept in our muscular tissues is for “locals only.” In other words, once it’s kept in muscle mass, it’s inefficient in being moved to various other areas of the body to offer gas. Instead, it has to be used on the website when your body can not push for another representative; this likely method is that the glycogen has been depleted in those muscle masses.
How much time does it take to diminish glycogen stores?
The type, strength, and duration of a workout can affect the time it takes to exhaust glycogen stores. Below are some general arrays:
Daily living activities: 12-22 hours
Reduced to moderate intensity workout (range operating): 90-120 mins
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT training): 20 mins
When you “struck a wall” during your exercise, this is partly due to glycogen deficiency. Typical signs and symptoms are an extreme loss of power as well as exhaustion. Glucose additionally creates ATP, which is the best body gas source. Percentages are present in the muscular tissues at any provided time. Also, they are used in anaerobic (lack of oxygen) workouts lasting much less than 10 seconds (i.e., a fast sprint) or as much as 30 seconds for an athlete. Other than this, ATP must be made with glycogenolysis.
What does glycogen do for muscular tissues?
Glycogen is the main energy-giver throughout the workout. The far better your body can keep glycogen, the far better it will certainly finish physical tasks. If reduced glycogen levels are offered in the body, you cannot exercise at high strength. Also, the duration of your training session will undoubtedly be restricted. Multiple studies show that tiredness, reduced efficiency, and signs and symptoms of overtraining relate to low-carb diet plans that cause glycogen depletion.
Why Carbohydrates Are Important for Exercise
Your mind consumes more than half of the body’s blood glucose through inactivity. Over an average day, your mind’s need for sugar represents around 20 percent of your body’s energy needs.
Diet plan and Glycogen
What you eat, as well as just how much you walk around, also affects glycogen manufacturing. The results are felt explicitly if you’re following a low-carb diet regimen, where the primary resource of sugar synthesis – carbohydrate – is suddenly limited.
When starting a low-carb diet regimen, your body’s glycogen shops can be severely diminished, and you might also experience signs of fatigue and mental dullness. These signs should diminish as soon as your body changes and begin restoring its glycogen shops.
Furthermore, any quantity of weight loss can have the same effect on glycogen stores. At first, you may experience a rapid decrease in weight. After some time, your weight may plateau and possibly also rise.
The phenomenon is partly because of the makeup of glycogen, which is mostly water. The water in these molecules accounts for 3 to four times the weight of the sugar itself.
As such, rapid glycogen exhaustion at the beginning of the diet regimen sets off water weight loss. Over time, glycogen shops are restored, and the water weight returns. When this happens, fat burning may stall or plateau.
Gains experienced at this phase are from water, not fat, and are just short-lived. Fat loss can proceed despite the temporary plateau impact.
Workout and Glycogen
The body can save around 2,000 calories of glucose as glycogen. For endurance athletes that burn that many calories in several hrs, the amount of saved glucose can be an impediment. When these professional athletes lack glycogen, their performance almost quickly begins to suffer – a state commonly described as “hitting the wall surface.”
If you’re undertaking a demanding workout regimen, there are several strategies endurance athletes make use of to stay clear of lowered performance you might locate handy.
What recovers glycogen?
When the body experiences the exhaustion of shops, it will certainly take around 24 hours to refuel (i.e., ingest, absorb, and convert food into glycogen). It is comprehended that carb-containing foods will aid in restoring shops the most successfully. When food is digested, sugar is produced. The pancreas recognizes this and creates insulin, a hormone that manages the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. Any glucose not utilized currently is routed to the liver to be saved as glycogen.
Should you load carb?
One way professional athletes keep large quantities of glycogen is with carbohydrate loading. This is when carbohydrate-rich dishes are eaten before an event. While this method may provide gas, it has occurred support because of the side effects of excess water weight and digestion issues. If you’re training for an occasion, such as a marathon, experiment with any diet regimen changes for weeks, even months, before the chance to see to it they help you.
A different approach utilized by some professional athletes is to minimize carbs during training. This causes a decrease in glycogen and also triggers the body to use fat stores for fuel instead. Therefore, trying a brand-new workout regularly is not the best idea if you are new to a low-carb diet regimen like the ketogenic diet (keto for brief). You can wind up with flu-like signs such as grogginess or an upset stomach. Go slow-moving and attempt not to make a lot of changes at the same time.
Before you try any extreme diet, such as the keto high-fat, low-carb one, we recommend you study and consult a physician.
Carb-loading
Some athletes eat extreme quantities of carbs before an endurance event. While added carbohydrates will undoubtedly provide sufficient gas, the technique has befallen chiefly favor as it can also bring about excess water weight and digestion concerns.
Consuming glucose gels: Power gels containing glycogen can be consumed before or as needed throughout an endurance event to boost blood glucose degrees.
Glycogen functions and statistical data
- Energy Storage and Regulation:
- Glycogen acts as a significant energy reservoir, with its degradation maintaining normal blood glucose levels and fuels muscle contraction1.
- The synthesis of glycogen, known as glycogenesis, is a multistep process that begins with converting glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, trapping glucose within the cell for later use2.
- Muscle Function:
- Studies have shown the role of glycogen content on insulin- and contraction-stimulated glucose uptake, glycogen synthase activation, and activation of signaling proteins in skeletal muscles3.
- Cellular Function and Health:
- Beyond energy storage, glycogen also plays critical roles in cell differentiation, signaling, redox regulation, and stemness under various physiological and pathophysiological conditions, as revealed by different glycogen storage diseases4.
- Tissue Composition:
- Glycogen makes up 6-10% of the liver and 1-2% of muscle by weight. This compositional difference emphasizes the importance of glycogen in these tissues’ metabolic processes5.
These functions underscore glycogen’s central role in maintaining energy homeostasis, supporting muscle function, and ensuring cellular health and function across various physiological contexts.
Latest Research-Backed Data
- Restoration of Muscle Glycogen and Functional Capacity: Role of …
- Date Published: Feb 23, 2018
- Summary: This article discusses the restoration of muscle glycogen and its role in functional capacity.
- Link to the article
- The Role of Brain Glycogen in Supporting Physiological … – Frontiers
- Date Published: Oct 17, 2019
- Summary: The article explores the role of brain glycogen in supporting physiological functions and highlights the significance of lactate in this context.
- Link to the article
- Fundamentals of glycogen metabolism for coaches and athletes – PMC
- Date Published: Feb 10, 2018
- Summary: This comprehensive article provides insights into the fundamentals of glycogen metabolism, emphasizing its importance for coaches and athletes.
- Link to the article
- Glycogen regulation and functional role in mouse white matter – PMC
- Date Published: Not specified
- Summary: The study investigates the regulation of glycogen and its functional role in mouse white matter.
- Link to the article
- The Role of Skeletal Muscle Glycogen Breakdown for Regulation of …
- Date Published: Not specified
- Summary: The article delves into the role of skeletal muscle glycogen breakdown in the regulation of insulin sensitivity.
- Link to the article
- Human brain glycogen content and metabolism: implications on its …
- Date Published: Not specified
- Summary: This research focuses on human brain glycogen content and metabolism, discussing its implications on brain function.
- Link to the article
These articles provide insights into the various roles of glycogen in different tissues, including muscles and the brain, and its significance in physiological functions and athletic performance.
FAQs
What is the primary role of glycogen?
Glycogen serves as a vital energy storehouse, fueling our body during physical exertions and maintaining blood glucose levels.
How is glycogen utilized in the body?
It’s broken down into glucose to provide quick energy, crucial during moderate to high-intensity physical activities.
Where is glycogen stored in the body?
Glycogen is primarily stored in the liver and muscles, ready to be converted into energy whenever needed.
How does glycogen support muscle function?
Glycogen provides the necessary fuel for muscle contractions, supporting endurance and performance during physical activities.
Why is glycogen important for brain function?
Glycogen stored in glial cells aids in maintaining glucose levels critical for normal brain function and responsiveness.
Conclusion
Ah, glycogen, our body’s behind-the-scenes powerhouse, silently fueling our every move, from sprinting for the bus to enduring a marathon. Its role? A reliable energy reservoir tucked away in our liver and muscles, springing into action when we need it most like a backstage crew ensuring the show goes on without a hitch1.
Much like how a car needs fuel to roar to life, our bodies rely on glycogen to keep the energy curtains up, especially when dietary carbs take a bow. And it doesn’t stop at muscles; glycogen plays a crucial encore in our brain, maintaining necessary glucose levels for sharp thinking on the fly.
Elite athletes, like Michael Phelps, have a special camaraderie with glycogen, banking on its energy storage to push through intense workouts and compete at the pinnacle of their game. It’s like having high-octane fuel in your tank, ready to blaze through the tracks1.
Now that you know the role of glycogen, are you ready to appreciate this silent powerhouse during your next workout? Your every sprint and lift is a testament to glycogen’s tireless energy supply. Go ahead, power through your day, and tip your hat to glycogen, the unsung hero in your energy tale!
References
Glycogen: What It Is & Function – Cleveland Clinic
Glycogen is a form of glucose, a main energy source that your body stores primarily in your liver and muscles.
The primary function of glycogen is to maintain a physiological blood glucose concentration.
Definition: Glycogen (for Teens) – Nemours KidsHealth
When the body needs a quick boost of energy or isn’t getting glucose from food, glycogen is broken down to release glucose into the bloodstream to …
What Is Glycogen? Storage, Function, Tests, and More – WebMD
Glycogen is a form of glucose that helps regulate your blood sugar levels. Your eating and exercise habits play a role in determining your …
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that stores energy in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the primary storage form …
The Role of Brain Glycogen in Supporting Physiological Function – Frontiers
In the hippocampus, glycogen is vital in supplying the neurons with lactate during memory formation.
As a veteran fitness technology innovator and the founder of GearUpToFit.com, Alex Papaioannou stands at the intersection of health science and artificial intelligence. With over a decade of specialized experience in digital wellness solutions, he’s transforming how people approach their fitness journey through data-driven methodologies.
